What is Arthritis / Rheumatism
Arthritis and rheumatism are terms often used to describe various conditions that affect the joints and cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. Here’s a breakdown of both:
1. Arthritis:
Arthritis is a broad term referring to a group of more than 100 diseases that affect the joints—the places where two or more bones meet. The most common forms include:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): A degenerative joint disease caused by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased joint flexibility.
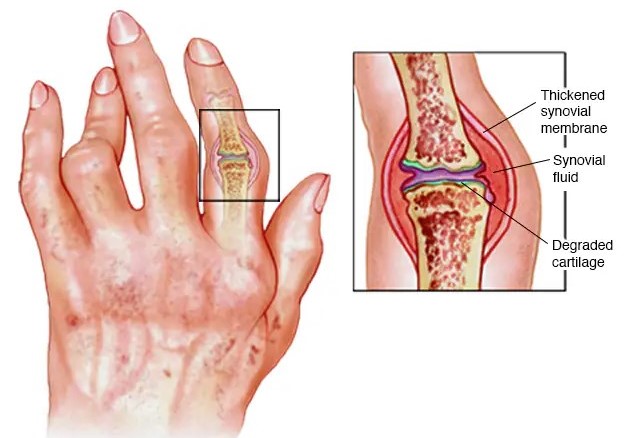
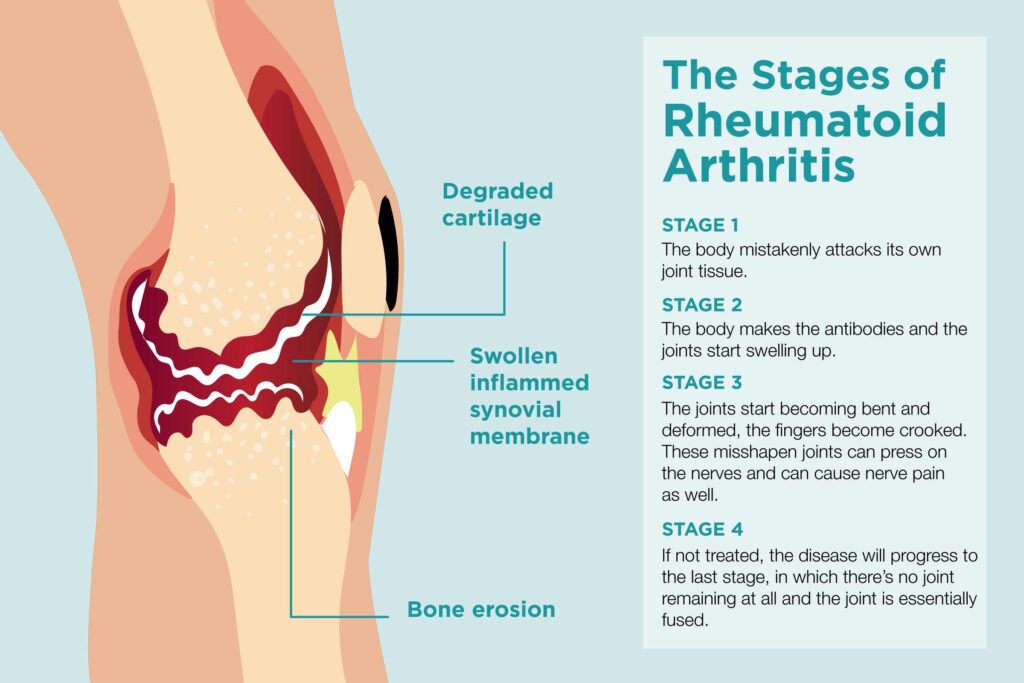
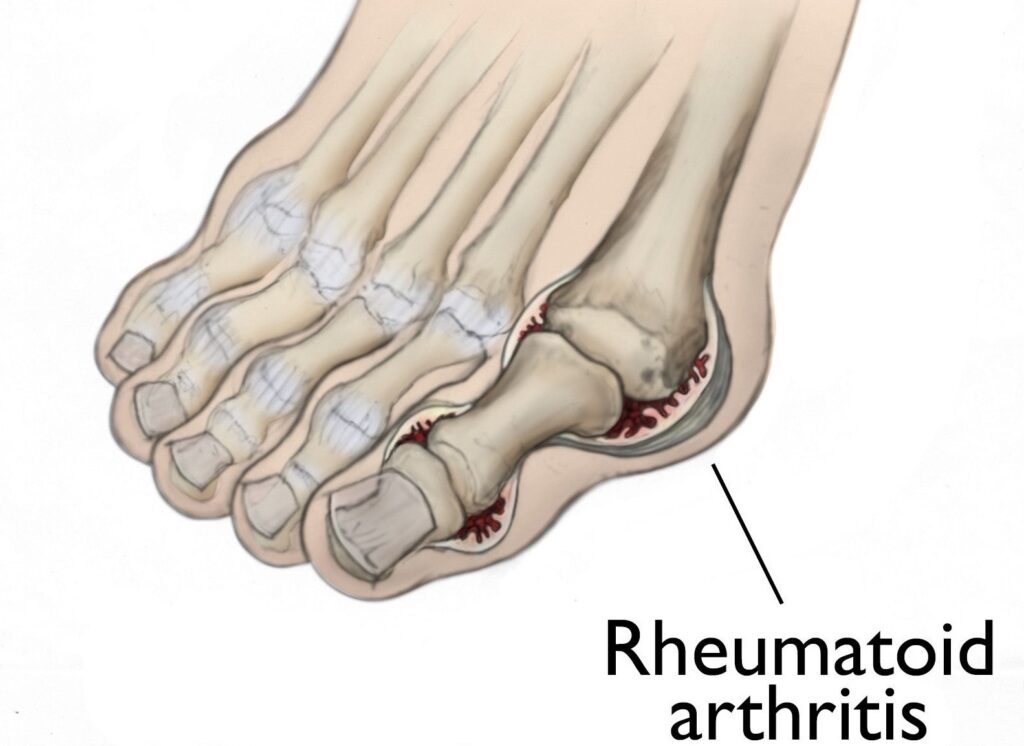
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage.
- Gout: A form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Occurs in some people with psoriasis, a skin condition, and causes joint inflammation.
Symptoms of arthritis generally include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. The severity and progression of the disease can vary from person to person.
2. Rheumatism:
Rheumatism is a more general term often used to describe any condition that causes chronic pain and inflammation in the muscles, joints, or connective tissues. It is commonly used as a lay term for disorders like arthritis, but it is not a specific diagnosis. The term includes:
- Rheumatic Diseases: Conditions that affect the joints, muscles, and connective tissues, including various forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
While “rheumatism” is sometimes used informally to refer to arthritis, it is broader and can refer to any condition involving inflammation or pain in the musculoskeletal system.
Causes of Arthritis / Rheumatism
The causes of arthritis and rheumatism can vary depending on the type of condition. Below are the primary causes for the most common forms:
1. Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and typically occurs as a result of wear and tear on the joints. It is generally linked to:
- Aging: As people get older, the cartilage that cushions the joints can deteriorate, leading to bone-on-bone friction and pain.
- Joint Injury: Previous injuries or trauma (e.g., fractures or ligament damage) can increase the risk of developing OA in the affected joint.
- Overuse of Joints: Repetitive motion or overuse in certain activities, especially jobs or sports that involve heavy lifting or strain on specific joints.
- Genetics: Family history may play a role, as some people may be genetically predisposed to developing OA.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts extra stress on weight-bearing joints (like knees and hips), which can contribute to cartilage breakdown.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, specifically the synovium (lining of the joints). Causes include:
- Genetics: Certain genes, such as the HLA-DRB1 gene, are associated with an increased risk of RA. However, not everyone with these genes will develop the disease.
- Immune System Dysfunction: In RA, the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues, causing inflammation and damage to the joints.
- Environmental Factors: Infections or exposure to certain environmental factors (such as smoking) may trigger or worsen RA in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Hormonal Factors: RA is more common in women, particularly during their childbearing years, suggesting that hormones might play a role in the development of the disease.
3. Gout
Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid in the blood, which forms crystals that deposit in the joints, leading to inflammation and severe pain. Causes include:
- High Uric Acid Levels: Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted by the kidneys. When the body produces too much or the kidneys cannot eliminate enough uric acid, it can build up and form crystals.
- Dietary Factors: Foods high in purines (such as red meat, shellfish, alcohol, and sugary beverages) can increase uric acid levels, leading to gout flare-ups.
- Obesity: Obesity increases the risk of high uric acid levels and decreases the ability of the kidneys to excrete it.
- Genetics: A family history of gout can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
4. Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is associated with psoriasis, a skin condition. It involves inflammation of the joints and the skin. Causes include:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis increases the risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Like RA, psoriatic arthritis is thought to be an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks healthy cells, leading to joint inflammation.
- Infections or Injury: Infections or physical trauma may trigger the onset of psoriatic arthritis in some people.
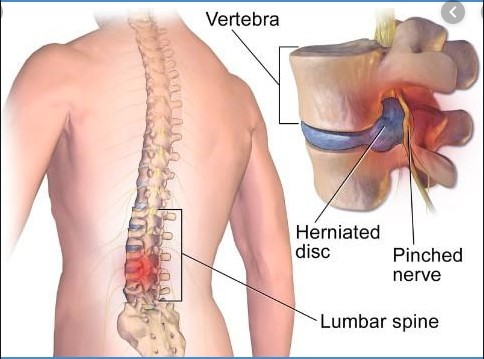
5. Ankylosing Spondylitis
This is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine and is related to inflammation in the joints and ligaments. Causes include:
- Genetics: The gene HLA-B27 is strongly associated with ankylosing spondylitis. However, not everyone with this gene develops the condition.
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system’s inflammatory response plays a role in the development of the disease.
6. Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – SLE)
Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, including the joints. Causes include:
- Genetics: A family history of lupus or other autoimmune diseases increases the risk.
- Hormones: Lupus is more common in women, suggesting that hormonal factors (like estrogen) may influence its development.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to sunlight, infections, or certain medications can trigger lupus flare-ups in people who are genetically predisposed.
7. Rheumatic Fever
This is an inflammatory disease that can develop after a strep throat infection. It can affect the joints, heart, skin, and nervous system. Causes include:
- Streptococcal Infection: A throat infection caused by Group A Streptococcus bacteria, if untreated, can trigger an immune response that leads to inflammation in various parts of the body, including the joints.
Effects of Arthritis / Rheumatism
The effects of arthritis and rheumatism can vary greatly depending on the type of condition and its severity. Both can cause significant physical discomfort and may lead to long-term complications if not properly managed. Below are some of the common effects:
1. Pain
- Chronic Pain: The most common and noticeable effect of arthritis and rheumatism is pain in the affected joints. This pain can range from mild to severe, and it may worsen over time, particularly with certain types of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
- Pain Flare-ups: In autoimmune forms like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, pain may come in sudden, intense flare-ups, often accompanied by swelling and redness in the affected joints.
2. Stiffness
- Morning Stiffness: Many people with arthritis or rheumatism experience stiffness, particularly in the mornings or after periods of inactivity. This stiffness can make it difficult to perform simple tasks, such as getting out of bed or walking.
- Reduced Range of Motion: The stiffness may progress over time, limiting the range of motion in the affected joints. This can hinder movement and reduce the ability to perform everyday activities.
3. Swelling and Inflammation
- Joint Swelling: Inflammatory types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, can cause noticeable swelling in the joints. This can be painful and may further restrict movement.
- Warmth and Redness: Inflamed joints may become red and warm to the touch due to increased blood flow and immune activity in the area.
4. Deformity and Joint Damage
- Progressive Joint Damage: If left untreated or poorly managed, some forms of arthritis, especially rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, can lead to permanent joint damage. The bones may erode, and the cartilage may wear away, leading to deformities.
- Deformities: In severe cases, joint deformities may develop, where the joints may become misshapen or misaligned. This can significantly impact function and quality of life.
- For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, the fingers and toes may become bent, and in osteoarthritis, the knees and hips may become misaligned.
5. Fatigue
- General Fatigue: Chronic inflammation, pain, and disrupted sleep can contribute to overall fatigue. People with inflammatory arthritis often experience tiredness, even after a full night’s rest.
- Exhaustion During Flare-ups: During flare-ups, when inflammation is at its peak, fatigue can worsen, making it even more difficult to carry out daily activities.
6. Loss of Function and Mobility
- Reduced Ability to Move: As joint pain and stiffness progress, people with arthritis may find it difficult to walk, stand, or engage in physical activities. The loss of mobility can affect daily life, including work, household tasks, and social activities.
- Difficulty with Fine Motor Skills: In conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, the small joints in the hands and fingers can become affected, leading to problems with gripping, writing, or handling objects.
7. Sleep Disruptions
- Pain Disrupting Sleep: The pain and discomfort from arthritis can disrupt sleep, leading to poor sleep quality. Lack of rest can exacerbate the other symptoms, including fatigue, mood changes, and pain sensitivity.
8. Complications in Other Body Systems
In some types of arthritis, especially those that are autoimmune (like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus), the disease can affect other systems in the body:
- Heart and Lungs: Rheumatoid arthritis, for example, has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and lung problems.
- Kidneys: Conditions like lupus and gout can damage the kidneys over time.
- Eyes: Some forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause eye problems, including dryness or inflammation.
9. Increased Risk of Other Health Problems
- Obesity: Reduced physical activity due to pain and immobility can lead to weight gain, which further exacerbates joint problems, especially in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
- Osteoporosis: Chronic inflammation, especially in rheumatoid arthritis, can lead to weakened bones (osteoporosis), increasing the risk of fractures.
Treatment of Arthritis / Rheumatism and Spondylosis
Looking for natural support for joint and spine health?
Our holistic wellness approach is designed to support comfort and mobility as part of a broader well-being strategy
Trusted by many across Nigeria seeking complementary care.
We offer supportive therapies that has been used traditionally to manage symptoms and improve well-being, including:
Acupuncture Therapy
Cupping Therapy (Wet & Dry)
Chiropractic Techniques
Heat Therapy
Let me discuss few of these therapies listed.
Acupuncture: It is India and Chinese way of managing bone degeneration etc., which has been in use for more than 2000 years.
Below are benefits of Acupuncture.
Benefits of Acupuncture for Arthritis / Rheumatism and Spondylosis
Pain Relief & Improved Function
Meta-analyses show acupuncture significantly reduces osteoarthritis-related pain and enhances functional mobility and quality of life—especially with treatments lasting more than four weeks.Acupuncture may trigger release of endorphins, enkephalins, and cortisol, helping reduce pain and inflammation.
- Benefits often appear shortly after sessions but may not persist in the long term, indicating that acupuncture may serve best as a complement to other treatments.
- A meta-analysis affirms acupuncture (including variations like electroacupuncture, moxibustion, warm needling) can alleviate pain, improve rheumatoid arthritis quality-of-life scores, tender joint counts, and reduce inflammatory markers.
Benefits of Cupping Therapy for Arthritis / Rheumatism and Spondylosis
Cupping therapy, an ancient treatment that uses suction to stimulate specific areas of the body, it is used as a complementary treatment for a variety of health conditions, including arthritis, rheumatism, and spondylosis.
Pain Relief: Cupping therapy helps to reduce pain by improving blood circulation in the affected areas. The suction from the cups creates a local inflammatory response that encourages the body to heal itself by increasing blood flow and oxygen to the tissues.
Reduction in Inflammation: For both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, cupping helps to alleviate inflammation. By improving circulation, it might reduce swelling around the joints, which is a common symptom of arthritis.
Improved Joint Mobility: Cupping can help improve range of motion in affected joints by easing muscle tension and reducing stiffness. This is particularly beneficial for those who experience restricted movement due to joint inflammation.
Muscle Relaxation: Cupping is known for its muscle-relaxing effects. Rheumatism often involves muscle pain and stiffness, and cupping therapy can help reduce muscle spasms and enhance flexibility.
Detoxification: cupping therapy helps with the removal of toxins from the body, which could be helpful for those suffering from rheumatic diseases, as it may reduce the burden on the immune system and help alleviate symptoms.
Improved Circulation: Rheumatic diseases are often associated with poor circulation, and cupping therapy can stimulate the blood vessels to improve the flow of oxygen and nutrients, helping to reduce pain and swelling.
Improved Posture and Alignment: Spondylosis can lead to a misalignment of the spine and poor posture. By increasing circulation and easing muscle tightness, cupping therapy promotes better spinal alignment and improve overall posture.
Nerve Relief: Since spondylosis can put pressure on nerves due to degenerative changes in the spine, cupping helps in reducing pressure on nerve endings, potentially providing relief from pain that radiates down the limbs (e.g., sciatica).
- etc.
OUR CLINIC ADDRESS
Electro Mart Building, U-turn Bus Stop, Abule Egba, Lagos, Nigeria.
08038690104 (CALL OR WHATSAPP)
VISITING HOURS FOR LAGOS RESIDENTS:
MONDAY- FRIDAY 8AM-5PM
SATURDAY: 9AM-3PM
Other Treatments We offer
